Last Updated on July 22, 2022
Today’s vehicles rely heavily upon a web of modules, intelligent devices, and wiring to operate in a safe and efficient manner. Each component and connection within these systems prove vital in more ways than one and must exhibit a high degree of integrity.
However, despite the implementation of cutting edge manufacturing practices, no vehicle is immune to the occasional electrical fault. Such faults can range in severity, resulting in anything from the sudden illumination of a check engine light to substantial drivability issues.
One such electrical error that can hamper a vehicle’s overall reliability, is that which is signified by diagnostic trouble code P0121. This fault code is indicative of issues within a vehicle’s throttle position circuit and can prove quite troubling to contend with.
Read on to learn more about diagnostic trouble code P0121, as well as how to proceed, should such an issue arise in the future.
What Does Code P0121 Mean?
Diagnostic trouble code P0121 indicates that your vehicle’s ECM/PCM has observed a circuit “A” value that is above or below its specified range. Simply put, a vehicle’s management software is programmed to anticipate certain voltages within an engine’s throttle position circuit.
When these voltages fall outside of this predetermined range, a fault code is registered. In the case of irregular voltage within the throttle position sensor’s “A” circuit, DTC P0121 is registered.
In many cases, the occurrence of such a fault code is met by an automatic system response. This generally comes in the form of the restriction of power via a vehicle’s management software, in an attempt to mitigate undue risk. While some vehicles will enter a “limp mode” of sorts, others will soldier on, albeit with often severe drivability issues.
Related Codes: P0122, P10123, P2135, P2138
Symptoms of Code P0121

Diagnostic trouble code P0121 is often accompanied by a number of additional symptoms. While not all of these symptoms will be present in every case, most are common enough to warrant further understanding and can prove noteworthy when attempting to diagnose the issue at hand.
The following are several of the most common symptoms associated with DTC P0121.
- Stalling
- Starting issues
- Lack of throttle response
- Erratic acceleration
- Reduced engine power
- Check engine light
Causes of Code P0121
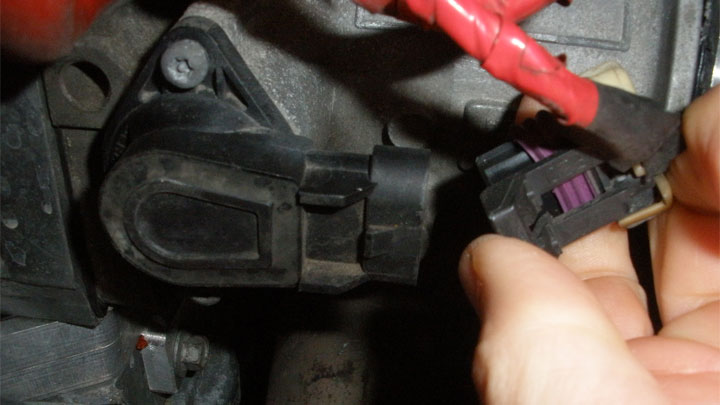
Diagnostic trouble code P0121 can be caused by a number of different issues, some of which are more common than others. Understanding the potential causes of DTC P0121, often allows one to expedite the diagnostic process as a whole.
The following are several of the most prominent causes of diagnostic trouble code P0121.
- Faulty or damaged throttle body
- Dirty throttle body
- Bad throttle position sensor
- Poor throttle position sensor connection
- Corroded pins in throttle position circuit-related connectors
- Open or shorted TPS circuit
Is Code P0121 Serious?
Diagnostic trouble code P0121 is generally regarded as being quite serious in nature, due to its possible ramifications toward a vehicle’s drivability.
In many instances, DTC P0121 is accompanied by a number of serious drivability-related symptoms, which can negatively impact one’s ability to commute in a safe and efficient manner.
Some of the most serious symptoms associated with DTC P0121 include stalling, reduced engine power, and erratic acceleration. As such, it is reasonable to believe that the root cause of DTC P0121 could actually leave one stranded, in the most severe of cases.
In any event, the root cause of diagnostic trouble code P0121 should be diagnosed and repaired at the first available opportunity. If you do not feel comfortable fixing such issues on your own, schedule an appointment with your local service center as soon as possible.
How to Fix Code P0121

The following steps can be followed when attempting to diagnose and remedy the root cause of diagnostic trouble code P0121. As always, one should always consult factory-specific service literature for their particular make and model of vehicle, before attempting any such repairs.
#1 – Check For Additional DTCs
Prior to beginning the diagnostic process, you should check for the presence of additional diagnostic fault codes. Any such fault codes that are discovered, should be thoroughly diagnosed and remedied before moving forward.
#2 – Visually Inspect TPS/Wiring
The diagnostic process begins by performing a thorough visual inspection of a vehicle’s throttle position sensor, and corresponding wiring.
Any damaged or frayed wires should be repaired, while damage to the TPS or throttle body itself will likely warrant replacement. Additionally, the pins of a vehicle’s TPS connector should also be checked for uniformity.
#3 – Clean Throttle Body
Next, an engine’s throttle body should be cleaned to remove excess carbon fouling. This can be accomplished through the use of a rag, saturated with a good throttle body cleaner.
Mechanical throttle bodies can be opened by hand, while electrically controlled units will often require removal to facilitate thorough cleaning. Additionally, some electronic throttle bodies require recalibration, following the completion of such a procedure.
#4 – Test Voltages Between Circuits
If DTC P0121 persists, further testing will be required in a bid to uncover an open or shorted circuit. This process will be accomplished through the use of a multimeter when working with a mechanical throttle body, and with a quality scan tool when testing an electronically controlled throttle body.
All data should be compared to minimum and maximum values provided by your vehicle’s manufacturer. If power/ground is present at the TPS, yet the TPS itself exhibits an “open” or “grounded” condition, sensor replacement will be necessary.




