Last Updated on November 16, 2022
In the modern era, automotive technicians now rely heavily upon data presented by a vehicle’s on-board diagnostic system, when attempting to diagnose and repair various issues. The vast majority of such issues are now addressed through the use of a quality scan tool, rather than by more traditional “hands-on” means.
A vehicle’s on-board diagnostic system relays diagnostic trouble codes or “DTCs” for short. These codes provide technicians with a general description of any fault that has been registered.
Each DTC is assigned a specific fault number, by which it is identified. While many of these faults are generic across all vehicle makes and models, others are specific to one particular manufacturer.
One such manufacturer-specific code is DTC P1000. Diagnostic trouble code P1000 primarily affects Ford and Jaguar models, though this code also applies to Kia, Land Rover, and Mazda makes as well.
Read on to learn more about diagnostic trouble code P1000, as well as how to diagnose and address the root cause of such a code.
What Does Code P1000 Mean?
In the majority of cases, diagnostic trouble code P1000 indicates that a vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system has been unable to complete its standard list of readiness checks.
These checks are typically run prior to startup, in a bid to identify any functional faults that might be present. Active faults are then registered and stored, often leading to the illumination of a check engine light.
Depending upon the make of the vehicle in question, this code might be listed or worded in a slightly different fashion. For example, Kia states that DTC P1000 means “System Diagnosis Incomplete”, while Mazda specifies the meaning of this code as “OBDII Drive Cycle Malfunction”.
Though the exact definition of DTC P1000 varies by manufacturer, the code’s meaning remains essentially the same. Simply put, the vehicle in question experienced a disruption when attempting to run its routine preoperative system self-checks. The exact reason for such a failure generally varies on a case-by-case basis.
Alternatively, this code can also refer to the inability of a vehicle’s on-board diagnostic system to establish full feedback from one or more system monitors during a given drive cycle.
Some monitors considered during such checks include the adaptive fuel monitor, misfire monitor, catalyst efficiency monitor, evaporative system monitor, and heated oxygen sensors monitor.
See Also: Code P0603, Code P0606, Code P2509
Symptoms of Code P1000
In almost every instance, a vehicle with an active P1000 DTC will be otherwise asymptomatic (no symptoms). This stands to reason, as DTC P1000 is not attempting to draw attention to a specific functionality-based issue.
Instead, this code is simply signaling a general failure of a vehicle’s OBD-II system to complete its readiness checks.
A vehicle with an active P1000 DTC should only experience additional symptoms if another DTC has been logged. In such a case, any symptoms that become evident will likely be connected to this secondary code, rather than DTC P1000.
Causes of Code P1000

There are several potential causes of DTC P1000. However, the root cause of such an issue often varies on a case-by-case basis and can differ slightly from one make and model of vehicle to the next.
The following are the most common causes of DTC P1000.
- Loss of connection with Engine Control Module
- Loss of battery voltage during self-check cycle
- OBD fault detected before completion of full drive cycle (Ford-specific)
- All diagnostic trouble codes have been cleared (Ford/Mazda/Jaguar)
Read Also: What is Limp Mode?
Is Code P1000 Serious?
Diagnostic trouble code P1000 is not considered to be serious in nature. Quite the contrary, a code of this nature often resolves on its own, without intervention of any type. Therefore, one can continue driving their vehicle as they otherwise would, without fear of impending issues.
The lone exception to this rule comes when another active code has been logged, in addition to DTC P1000. In such instances, all additional codes should be diagnosed and remedied at the first available opportunity.
Doing so should fast-track the clearing of DTC P1000, by alleviating possible OBD-II errors.
How to Fix a Code P1000
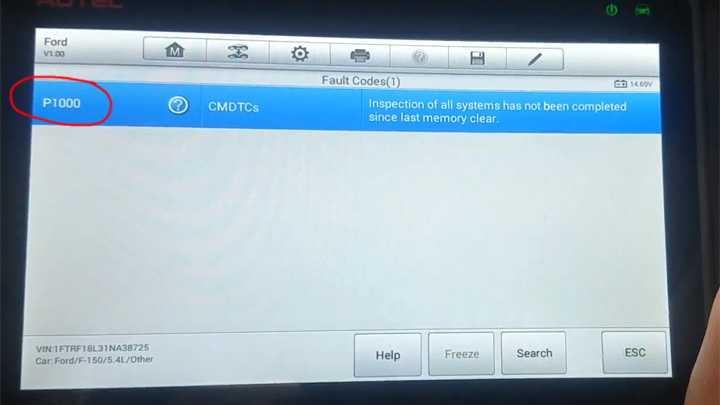
Due to the nature of diagnostic trouble code P1000, there is little need for actual diagnosis and repair. In fact, in the absence of additional trouble codes, DTC P1000 will clear on its own, without further intervention.
All that is required in order for this to happen, is the completion of a full system readiness check during a vehicle’s next drive cycle.
Nonetheless, it is important to ensure that no additional trouble codes are present. This can be accomplished with the use of any good quality OBDII scan tool. The presence of additional trouble codes often indicates a larger issue, wherein DTC P1000 simply indicates that another fault has been identified and logged.
This situation is best addressed by thoroughly diagnosing and repairing the root cause of any additional diagnostic trouble codes that are present. Upon doing so, DTC P1000 should be cleared as a secondary result of such repairs, though this process can take several drive cycles to complete.
If DTC P1000 remains persistent, the use of factory-specific software might be required. Using software of this nature allows one to manually command a full series of readiness checks. Once such checks are completed, P1000 should be cleared.
Such software can also be used to direct an individual through the “drive cycle” procedure for their particular vehicle. Following this procedure satisfies the criteria required to successfully complete a system self test, thereby clearing trouble code P1000 in the process.




