Last Updated on July 29, 2022
Today’s diesel engines are far more complex than those of yesteryear. Though the principle of compression-ignited combustion remains unchanged, most modern diesel engines come equipped with an array of secondary components, intended to reduce noxious emissions output. While the notion behind the use of these components is novel, at times, such efforts prove problematic.
Aftertreatment system failures now serve as the number-one mechanical complaint among diesel owners, often accounting for the illumination of numerous warning lights. One such warning light that is quite common among late model diesel-powered cars and trucks, is that which relates to a vehicle’s diesel particulate filter (DPF) light.
The sudden illumination of a vehicle’s diesel particulate warning light often spells trouble, especially if illuminated continuously for more than two consecutive start-cycles. In fact, issues of this nature often result in restricted performance, or complete engine shutdown, both of which have the potential to leave a motorist stranded.
Read on to learn more about the meaning behind the dreaded diesel particulate warning light, as well as how to address such issues should they arise in the future.
What is a Diesel Particulate Filter?
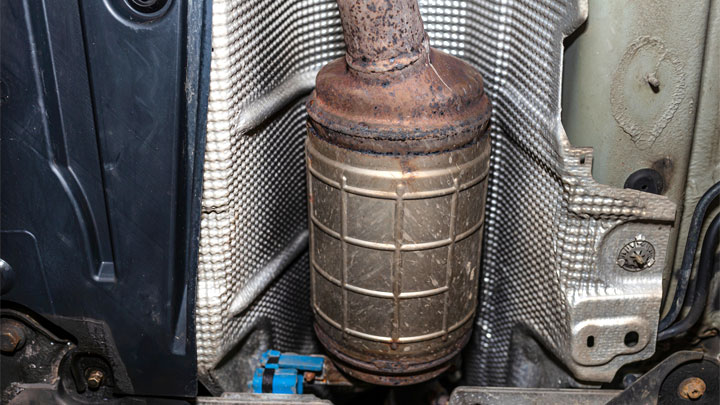

A diesel particulate filter is a specialized after-treatment device, which traps particulate matter produced as a byproduct of diesel combustion. This particulate matter most often materializes in the form of soot or ash.
Prior to the implementation of DPF technology, this particulate matter was expelled into the environment, via a truck’s exhaust.
The internal composition of a diesel particulate filter is made up of heavy-duty ceramic substrate, formed into a tight honeycomb pattern. This honeycomb effectively traps particulate matter, thereby preventing it from passing through the exhaust system in its entirety.
With time, a vehicle’s DPF becomes soot-loaded, thereby requiring regeneration or automatic cleaning. The process of regeneration is typically conducted as called for by an engine’s ECM/PCM and takes place without the need for driver interaction. This occurs in various stages, referred to as active and passive regeneration.
Why Does the DPF Light Come On?
A diesel particulate light illuminates to inform motorists that an engine’s passive regeneration has failed, thereby signifying the need for active regeneration.
A DPF utilizes a series of pressure differential switches and backpressure sensors to determine soot loading. A vehicle’s DPF warning light is illuminated when soot loading approaches a critical level.
While passive regeneration takes place on a continual basis, active regeneration is a more aggressive form of automated DPF cleaning, which requires a certain number of criteria to be met. The most important of these criteria is that an engine must reach full operating temperature prior to entering active regeneration, at which time fuel will be injected into the after-treatment system.
Upon entering regeneration of this level, a vehicle must also be continuously driven at highway speeds for up to 45 minutes. Delayed stoppage in route will often abort the active regeneration process, thereby yielding unsatisfactory results.
Most vehicles also display an alternative version of their DPF warning light, right before a truck derates, or enters limp mode. Alternatively, some vehicles, such as Duramax-equipped Chevrolet trucks, will display a warning on their integrated message center. Upon reaching this critical stage in soot loading, there is little that a motorist can do, without taking their vehicle to an authorized service center.
Can You Continue Driving With the DPF Light On?

In most cases, you can continue driving with a vehicle’s DPF warning light illuminated. In fact, most manufacturers recommend driving continuously at highway speed when such a warning light is illuminated, as doing so should force a vehicle into an active regeneration cycle.
However, if a vehicle’s DPF warning light begins to flash, or changes from yellow to red in color, one should pull off to a safe place as soon as possible. This generally indicates that a vehicle is about to enter severe derate, or shutdown.
If any driving were to take place at this stage, it should be for no further than required to reach an authorized service center.
Diesel Particulate Filter Cleaning Cost
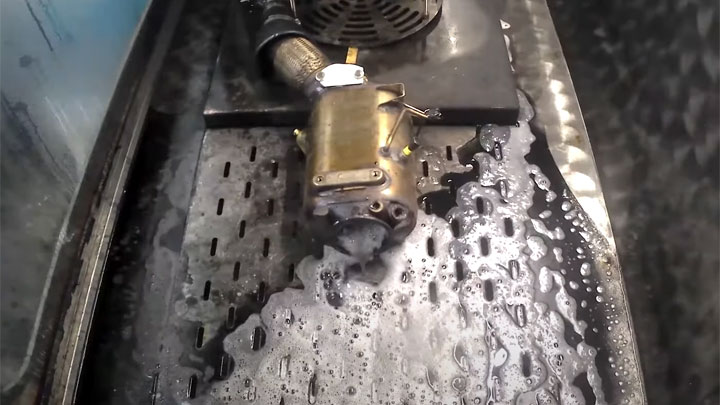

The most suitable means of returning your vehicle to service following DPF-related issues is to have the diesel particulate filter expertly cleaned.
This typically involves taking your vehicle to an authorized service center, where the DPF itself will be removed and cleaned with specialized equipment. This can be quite costly, especially if all DPF removal and installation are conducted in-house.
Luckily, the cost of DPF cleaning has begun to decline slightly over the past several years. In most cases, a DPF filter can be expertly cleaned for approximately $500-$1,000. However, the cost of this service increases significantly, when one considers the labor time required to remove and install a DPF.
The labor required for removal and installation of a vehicle’s DPF generally totals to somewhere between 3-5 hours, depending on the year, make, and model of vehicle in question. With average hourly shop labor rates now exceeding $100, such costs can easily reach the $500 mark.
Can I Clean the DPF Myself?
Short of driving for an extended period of time at highway speeds to force an active regeneration cycle, there is little that one can do to clean their vehicle’s DPF filter themselves.
In fact, properly cleaning a face-plugged DPF filter requires the use of specialized equipment and chemicals, most of which are quite expensive and difficult to come by for the average motorist.
Additionally, attempting to clean a vehicle’s DPF can cause a number of secondary issues. Further damage to a DPF filter can actually result from improper cleaning practices or the use of unauthorized chemicals.
Likewise, most manufacturers will void a vehicle’s after-treatment system warranty in its entirety, if it has been tampered with by anyone other than a certified technician.
How Long Does the Filter Last?
The exact lifespan of a Diesel Particulate Filter varies, based on a number of factors. The most pertinent of these factors include the type of driving that is most frequently conducted, the frequency of vehicle maintenance, and the general upkeep and cleaning of a DPF filter at specified intervals.
However, most Diesel Particulate Filters last for at least 100,000 miles, with few, if any issues. In rare cases, where the bulk of a vehicle’s miles can be attributed to highway driving, a DPF can even last significantly longer.
Diesel Particulate Filter Replacement Cost
Best places to order parts? See: 19 Best Online Auto Parts Stores

Diesel Particulate Filter replacement tends to be rather expensive, tallying up to quite the bill by the end of such service. In fact, the price of DPF cleaning has dropped considerably over the past few years, making it the much preferred option over eventual replacement.
While the cost of a DPF filter itself is quite exponential, this price is only compounded by additional labor costs accrued during removal and installation.
On average, a new diesel particulate filter costs somewhere in the range of $2,000-$8,000. The lower extreme of this range is largely representative of DPF filters found on diesel cars and pickups, while the upper end of this spectrum applies to larger on-highway vehicles, such as semis and dump trucks.
As stated, this price does not include the cost associated with DPF removal and installation. This labor is billed by the hour, based upon estimated industry labor standards. For this reason, it is best to factor in an additional $300-$500, on top of the cost of the new diesel particulate filter itself.
What is a DPF Delete Kit? (Should I Get One?)
As its name would suggest, a DPF delete kit is used to eliminate a vehicle’s stock DPF, and in many cases, a number of additional after-treatment components as well. However, the true extent of such kits differs considerably by manufacturer and availability.
Installation of a DPF delete kit also tends to require a customized tune to be entered into a vehicle’s ECM/PCM. This is due to the fact that a vehicle’s operational software must be tricked into overlooking various sensors utilized by the after-treatment system when a stock DPF is removed. If not, a host of driveability-related concerns can arise.
While DPF delete kits were once extremely popular, they have now come under increased scrutiny by the federal government. This is due to the fact that the removal of any government mandated smog-reduction equipment is against federal law. As such, one is subject to penalty, if the installation of such equipment is observed by federal officials.
For this reason, many automotive shops now refuse to install DPF delete kits of any kind, in an effort to prevent any unnecessary liability. There are also far fewer DPF delete kits currently on the market than were once available. Those that are still commercially available, are marketed for ¨off-road use only¨.




